Syllabus:
- Financial Market Regulation
- Central Bank & its Functions
- Conduct of Monetary Policy
- Financial Services: Meaning, scope & types
- Characteristics of Financial Services
- Causes for financial innovations
- Financial services & promotion of industries
- Financial service industries in Nepal
Financial Market Regulation
Financial market regulation is essential for ensuring the stability, transparency, and integrity of a country's financial system. The following are the principal regulatory agencies in Nepal and their respective roles:
- Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB): As the central bank, NRB regulates all depository institutions, including commercial banks, development banks, finance companies, micro financial institutions, and infrastructure development banks. It oversees the establishment and operations of these institutions to maintain financial standards and practices.
- Securities Board of Nepal: This board regulates organized exchanges, financial markets, and derivative markets. It ensures the establishment and operations of these markets adhere to standards that promote transparency, fairness, and efficiency, fostering investor confidence.
- Nepal Insurance Authority (NIA): NIA oversees life, non-life, and reinsurance insurance companies. It regulates their establishment and operations to ensure solvency and the ability to meet obligations to policyholders, protecting consumers.
- Department of Cooperatives: This department regulates all types of cooperatives, focusing on their establishment and operations. By doing so, it ensures cooperatives operate sustainably and contribute to financial inclusion.
- Deposit and Credit Guarantee Fund (DCGF): The DCGF insures deposits up to Rs 300,000 per depositor at commercial banks and financial institutions. This insurance mechanism enhances confidence in the banking system and contributes to financial stability.
- Company Registrar Office (CRO): The CRO regulates all companies registered with it, ensuring they comply with legal and regulatory requirements. This oversight helps maintain transparency and accountability in the corporate sector.
- Credit Information Bureau (CIB) of Nepal: The CIB provides credit information to banks and financial institutions. This service is crucial for assessing credit risk and making informed lending decisions, supporting the health of the financial system.
These regulatory agencies collectively contribute to the robustness of Nepal's financial market by ensuring that all financial activities are conducted in a safe, sound, and ethical manner.
Central Bank & Its Functions
The central bank is a national financial institution responsible for managing the monetary system of a country. Nepal Rastra Bank is the central bank of Nepal. It plays a crucial role in maintaining economic stability and fostering economic growth. Here are the detailed functions:
- Carrying Out Monetary Policy: The central bank controls the money supply and interest rates to achieve economic objectives such as controlling inflation, ensuring full employment, and fostering economic growth. By adjusting interest rates and using tools like open market operations and reserve requirements, the central bank can influence borrowing, spending, and investment in the economy.
- Supervision and Regulations: The central bank supervises and regulates commercial banks and other financial institutions to ensure they operate safely and soundly. This includes setting standards for banking practices, monitoring financial health, and enforcing compliance with laws and regulations. This supervision helps prevent financial crises and protects consumers.
- Maintaining Stability of the Financial System: The central bank monitors and manages risks that could threaten the stability of the financial system. It identifies potential financial vulnerabilities and implements measures to mitigate them, ensuring that the financial system remains resilient to shocks and capable of supporting economic activity.
- Maintaining and Improving the Payments Mechanism: The central bank ensures that payment systems, including checks, electronic transfers, and other payment methods, operate smoothly and efficiently. It works to improve these systems to facilitate safe, secure, and fast transactions, which are essential for the functioning of the economy.
- Issue of Paper Money and Coins: The central bank has the exclusive right to issue the nation's currency. It ensures that there is an adequate supply of paper money and coins to meet the public's demand, and it also designs and produces currency to prevent counterfeiting.
- Banker, Agent, and Advisor to the Government: The central bank manages the government's accounts, facilitates its financial transactions, and provides economic advice. It helps the government in executing its financial operations, such as issuing bonds, and offers guidance on economic policy based on its expertise and analysis.
- Custodian of Banks: The central bank holds reserves from commercial banks and other financial institutions. By doing so, it ensures that these institutions have sufficient liquidity to meet their obligations and can support the smooth functioning of the banking system.
- Custodian of Foreign Currency: The central bank manages the country's foreign exchange reserves, which are used to stabilize the national currency and support international trade. It intervenes in foreign exchange markets to influence exchange rates and ensure a stable economic environment.
- Lender of Last Resort: The central bank provides funds to banks and financial institutions in times of financial distress to prevent their failure. This function helps maintain confidence in the banking system and prevents bank runs and widespread financial panic.
- Clearing House Functions: The central bank facilitates the settlement of inter-bank transactions by acting as a clearinghouse. It ensures that funds are transferred efficiently and accurately between banks, which is essential for the smooth operation of the financial system.
Conduct of Monetary Policy
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by a central bank to control the money supply and interest rates in an economy. Its primary objective is to achieve macroeconomic goals such as controlling inflation, managing employment levels, and fostering economic growth. By manipulating monetary instruments, the central bank can influence economic activity, stabilize the financial system, and ensure sustainable economic development.
Goals of Monetary Policy
- Economic Growth: The central bank aims to create a conducive environment for economic expansion by ensuring a stable money supply and favorable interest rates. By promoting investment and consumption, monetary policy helps increase production and GDP growth.
- High Employment: One of the key objectives of monetary policy is to achieve and maintain high levels of employment. By lowering interest rates and increasing the money supply, the central bank can stimulate economic activity, leading to job creation and reduced unemployment.
- Financial Market and Institution Stability: Ensuring the stability of financial markets and institutions is crucial for the overall health of the economy. The central bank monitors and addresses risks that could lead to financial crises, thereby maintaining confidence in the financial system.
- Price Stability: Controlling inflation is a critical goal of monetary policy. By managing the money supply and interest rates, the central bank aims to keep inflation at a moderate and stable level, protecting the purchasing power of the currency.
- Interest Rate Stability: The central bank seeks to stabilize interest rates to reduce uncertainty and encourage long-term investment and borrowing. Stable interest rates contribute to predictable economic conditions, which are beneficial for businesses and consumers alike.
- Exchange Rate Stability: Maintaining a stable exchange rate is essential for fostering international trade and investment. The central bank may intervene in the foreign exchange market to prevent excessive volatility and ensure a stable currency value.
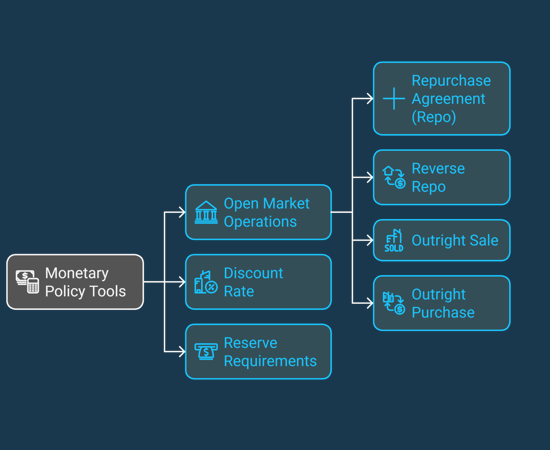
Tools of Monetary Policy
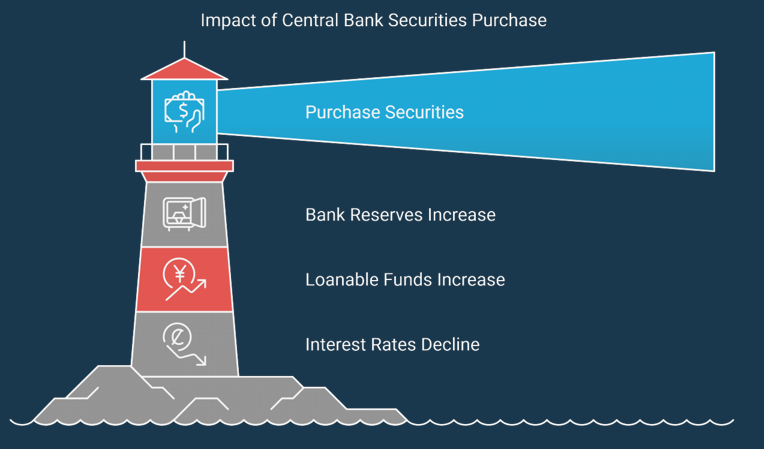
1. Open Market Operations (OMOs): Open market operations involve the buying and selling of government securities in the open market to regulate the money supply and influence interest rates. There are different types of OMOs:1.1 Repurchase Agreement (Repo): In a repo, the central bank purchases securities with an agreement to sell them back at a later date. This temporarily increases the money supply and lowers short-term interest rates.
1.2 Reverse Repo: In a reverse repo, the central bank sells securities with an agreement to buy them back later. This temporarily decreases the money supply and raises short-term interest rates.
1.3 Outright Purchase: The central bank buys securities outright, permanently increasing the money supply and lowering interest rates.
1.4 Outright Sale: The central bank sells securities outright, permanently decreasing the money supply and raising interest rates. 2. Discount Rate or Bank Rate: The discount rate (or bank rate) is the interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow funds from the central bank. By changing the discount rate, the central bank can influence the cost of borrowing and lending in the economy. Lowering the discount rate makes borrowing cheaper, stimulating economic activity, while raising it makes borrowing more expensive, cooling down the economy.
3. Reserve Requirement: The reserve requirement is the percentage of deposits that commercial banks must hold as reserves, either in their vaults or at the central bank. By adjusting the reserve requirement, the central bank can control the amount of money available for lending. Lowering the reserve requirement increases the money supply, while raising it decreases the money supply.
The servicces offerred by service industry like bank and financial institutions, insurance company, investment companies, etc.
Banking Services
- Definition: These are services provided by banks to their customers.
- Examples: Savings accounts, checking accounts, loans, credit cards, and mortgages.
- Purpose: To help individuals and businesses manage their money, make transactions, and access credit.
Investment Services
- Definition: These services help individuals and institutions invest their money to earn returns.
- Examples: Stockbroking, mutual funds, retirement accounts, and investment advice.
- Purpose: To grow wealth over time through investments in stocks, bonds, and other assets.
Insurance Services
- Definition: These services provide financial protection against risks and uncertainties.
- Examples: Life insurance, health insurance, property insurance, and auto insurance.
- Purpose: To safeguard individuals and businesses from financial loss due to unforeseen events.
Financial Planning and Advisory
- Definition: These services offer personalized advice on managing finances and achieving financial goals.
- Examples: Retirement planning, tax planning, estate planning, and budgeting.
- Purpose: To help individuals and businesses plan for the future and make informed financial decisions.
Asset Management Services
- Definition: These services involve managing investments on behalf of clients.
- Examples: Portfolio management, fund management, and investment advisory.
- Purpose: To optimize returns and manage risks by professionally handling clients' investment portfolios.
Payment and Settlement Services
- Definition: These services facilitate the transfer of money between parties.
- Examples: Electronic funds transfers (EFT), wire transfers, payment processing for online transactions.
- Purpose: To ensure secure and efficient transfer of funds in various transactions.
Wealth Management Services
- Definition: These services provide comprehensive financial planning and investment management for high-net-worth individuals.
- Examples: Investment management, financial planning, estate planning, and tax advice.
- Purpose: To preserve and grow the wealth of affluent clients through a holistic approach to financial management.
Corporate and Investment Banking
- Definition: These services cater to the financial needs of businesses and large institutions.
- Examples: Corporate loans, mergers and acquisitions (M&A) advisory, underwriting, and capital raising.
- Purpose: To support corporate clients with financing, strategic advice, and complex financial transactions.
The scope of financial services, as illustrated in the figure, is categorized into two main groups: Modern Activities and Traditional Activities.
Modern Activities
- Digital Banking: Offering banking services through digital platforms.
- Fintech Solutions: Innovative technology solutions for financial services.
- Wealth Management: Financial advisory and planning services to manage wealth.
- Project Advisory Services: Expertise in project planning and execution.
- Merger and Acquisition: Services related to business mergers and acquisitions.
Fund-Based Activities: Traditional financial services involving funds.
Non Fund-Based Activities: Services that do not directly involve handling funds.
- Remittance Sector: This sector deals with the transfer of money by individuals working abroad back to their home country. It is a significant contributor to Nepal's economy, helping to support families and local communities.
- Banking Sector: This encompasses traditional banking services such as savings accounts, loans, and other financial transactions. Banks play a vital role in financial intermediation, facilitating investment and consumption in the economy.
- Microfinance Institutions: These institutions provide small-scale financial services to low-income individuals or groups who typically do not have access to conventional banking services. They aim to promote financial inclusion and support entrepreneurship at the grassroots level.
- Cooperative Sector: Cooperatives are member-owned entities that provide financial services to their members. They operate based on principles of mutual assistance, and they help in mobilizing savings and providing credit in rural and urban areas.
- Capital Market: This sector involves the buying and selling of equity (stocks) and debt (bonds) instruments. It is essential for raising capital for businesses and providing investment opportunities for individuals and institutions.
- Insurance Sector: Insurance companies offer financial protection against various risks, such as health issues, accidents, and property damage. They play a critical role in risk management and financial stability.
These sectors collectively contribute to the economic development of Nepal by providing diverse financial services, fostering financial inclusion, and supporting both individual and corporate financial needs.








sabai chapter ko halna paryo note
ReplyDeleteThank you sir
ReplyDeletenumerical ko solution khoi ta practice wala
ReplyDeleteAru chapter ko ni note haldini nw theory haru
ReplyDeletePost a Comment
Do Leave Your Comments